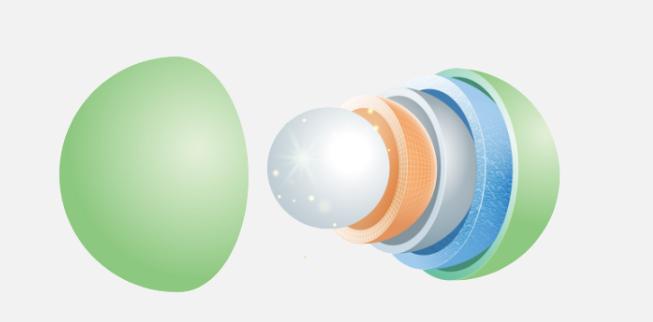
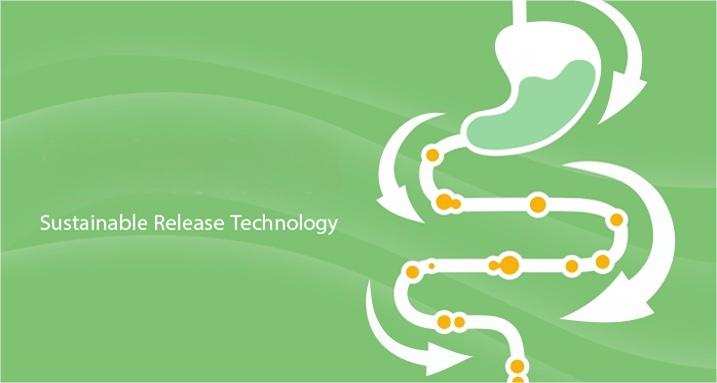
The popular "microencapsulated" nutritional ingredients in the market.
Typical ingredients include vitamins, minerals, probiotics, Omega-3, polyunsaturated fatty acids, carotenoids, etc.
(1) Vitamin & Mineral Microcapsules Powder
Vitamin raw materials generally have the problem of "easily oxidizing and unstable activity", especially vitamins A, C, D, and E, which are highly susceptible to the influence of ultraviolet rays, pH changes, temperature fluctuations, and even pasteurization processes, resulting in degradation of active ingredients and loss of nutritional value. Through microencapsulation technology, a protective coating can be formed on the surface, achieving multiple barriers and effectively extending the shelf life and nutritional validity of the product.
In contrast, mineral-based raw materials face another set of challenges: they have a bitter taste, a strong metallic flavor, and low bioavailability. For example, components such as iron, zinc, magnesium, and calcium. Through microcapsule encapsulation, the flavor experience can be optimized, and the release rate can be regulated, making them better suited for applications in functional beverages, gummies, powders, and other dosage forms.